A botnet (AKA a zombie army) is a number of Internet computers that, although their owners are unaware of it, have been set up to forward transmissions (including spam or viruses) to other computers on the Internet. Any such computer is referred to as a zombie - in effect, a computer "robot" or "bot" that serves the wishes of some master spam or virus originator. Most computers compromised in this way are home-based. According to a report from Russian-based Kaspersky Labs, botnets -- not spam, viruses, or worms -- currently pose the biggest threat to the Internet. A report from Symantec came to a similar conclusion.
Computers that are coopted to serve in a zombie army are often those whose owners fail to provide effective firewalls and other safeguards. An increasing number of home users have high speed connections for computers that may be inadequately protected. A zombie or bot is often created through an Internet port that has been left open and through which a small Trojan horse program can be left for future activation. At a certain time, the zombie army "controller" can unleash the effects of the army by sending a single command, possibly from an Internet Relay Channel (IRC) site.
The computers that form a botnet can be programmed to redirect transmissions to a specific computer, such as a Web site that can be closed down by having to handle too much traffic - a distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack - or, in the case of spam distribution, to many computers. The motivation for a zombie master who creates a DDoS attack may be to cripple a competitor. The motivation for a zombie master sending spam is in the money to be made. Both of them rely on unprotected computers that can be turned into zombies.
According to the Symantec Internet Security Threat Report, through the first six months of 2006, there were 4,696,903 active botnet computers.
Credits to:
http://www.readwriteweb.com/archives/is_your_pc_part_of_a_botnet.php
http://searchsecurity.techtarget.com/definition/botnet
Wednesday, 16 November 2011
Friday, 11 November 2011
Seven Poll Result Analysis
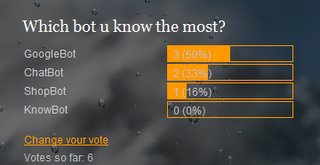
This picture below is previous week poll analysis. We are discussed the question of which bot does your know more about it. Most of the voters voted "Googlebot".

In the conclusion , there are 6 persons voted the poll, 3 persons voted "Google Bot.". This means that most of the people know more in google bot. 2 persons voted "chat bot", not much of voter vote about chat bot, because google bot are more popular that chat bot.And there are only 1 ppl know what is shop bot. For the know bot there are not people know about what is know bot, to look more information about know bot can get information fromw our blog. If you have any question u can send a mail to us to leave a comment here. Besides, we will always share more information about Web bot to you!
Thursday, 10 November 2011
Computer game bot
A bot, most prominently in the first-person shooter types (FPS), is a type of weak AI expert system software which for each instance of the program controls a player in deathmatch, team deathmatch and/or cooperative human player. Computer bots may play against other bots and/or human players in unison, either over the Internet, on a LAN or in a local session.Features and intelligence of bots may vary greatly, especially with community created content. Advanced bots feature machine learning for dynamic learning of patterns of the opponent as well as dynamic learning of previously unknown maps – whereas more trivial bots may rely completely on lists of waypoints created for each map by the developer, limiting the bot to play only maps with said waypoints. Using bots is incidentally against the rules of all of the current main Massively multiplayer online role-playing games (MMORPGs).
In Multi-User Domain games (MUDs), players may utilize bots to perform laborious tasks for them, sometimes even the bulk of the gameplay. While a prohibited practice in most MUDs, there is an incentive for the player to save his/her time while the bot accumulates resources, such as experience, for the player character.
Aim Bot
An aimbot (sometimes called "auto-aim") is a type of computer game bot used in first-person shooter games to provide varying levels of target acquisition assistance to the player. It is sometimes incorporated as a feature of a game (where it is usually called "auto-aim" or "aiming assist"). However, making the aim-bot more powerful in multiplayer games is considered cheating, as it gives the user an advantage over unaided players.
Aimbots have varying levels of effectiveness. Some aimbots can do all of the aiming and shooting, requiring the user to move into a position where the opponents are visible; this level of automation usually makes it difficult to hide an aimbot—for example, the player might make inhumanly fast turns that always end with his or her crosshairs targeting an opponent's head. Numerous anti-cheat mechanisms have been employed by companies such as Valve to prevent their use and avoid the accusations.
Some games have "auto-aim" as an option in the game. This is not the same as an aimbot; it simply helps the user to aim when playing offline against computer opponents usually by slowing the movement of 'looking/aiming' while the crosshair is on or near a target. It is common for console FPS games to have this feature to compensate for the lack of precision in analog-stick control pads.
Credits to:
http://gamebots.sourceforge.net/
http://mmohuts.com/review/bots
In Multi-User Domain games (MUDs), players may utilize bots to perform laborious tasks for them, sometimes even the bulk of the gameplay. While a prohibited practice in most MUDs, there is an incentive for the player to save his/her time while the bot accumulates resources, such as experience, for the player character.
Aim Bot
An aimbot (sometimes called "auto-aim") is a type of computer game bot used in first-person shooter games to provide varying levels of target acquisition assistance to the player. It is sometimes incorporated as a feature of a game (where it is usually called "auto-aim" or "aiming assist"). However, making the aim-bot more powerful in multiplayer games is considered cheating, as it gives the user an advantage over unaided players.
Aimbots have varying levels of effectiveness. Some aimbots can do all of the aiming and shooting, requiring the user to move into a position where the opponents are visible; this level of automation usually makes it difficult to hide an aimbot—for example, the player might make inhumanly fast turns that always end with his or her crosshairs targeting an opponent's head. Numerous anti-cheat mechanisms have been employed by companies such as Valve to prevent their use and avoid the accusations.
Some games have "auto-aim" as an option in the game. This is not the same as an aimbot; it simply helps the user to aim when playing offline against computer opponents usually by slowing the movement of 'looking/aiming' while the crosshair is on or near a target. It is common for console FPS games to have this feature to compensate for the lack of precision in analog-stick control pads.
Credits to:
http://gamebots.sourceforge.net/
http://mmohuts.com/review/bots
IRC BOT

What is an IRC bot?
An automated client:
To an IRC server, an IRC bot is virtually indistinguishable from a regular IRC client (i.e., a person using a program such as X-Chat, mIRC, or ircii). However, there's no person typing behind an IRC bot. It only makes automated responses, based on (usually) what is happening on IRC. An IRC bot can do things based on public messages, private messages, pings, or any other IRC event. But a bot isn't limited to the world of IRC. It can talk to a database, the web, a filesystem, or anything else you may imagine.
Examples:
Here are some common IRC bots that you may have seen in your travels already:
File serving: This type of bot emulates an FTP program by interfacing with a filesystem. Users talk to the bot using private messages with commands like "ls" and "get". The user can send and receive files using DCC (a part of IRC that allows the initiation of peer-to-peer file transfers).
Channel administration: This bot maintains a list of channel ops (people who run the channel) and makes sure they stay in control of it, even if individual people are disconnected. They may also kick people from the channel who violate its etiquette (e.g., talking in all caps, using colors, flooding, etc.)
Games: Some bots will allow the people in the channel to text-based games. We'll learn later how to program a trivia bot.
What you need to program an IRC bot
1. Perl
2. Net::IRC Module
3. IRC server
HelloBot
HelloBot is a greeting bot. When a user, let's give him the nick "Joe," joins a channels, HelloBot will say "Hello, Joe!" When Joe leaves, HelloBot will say "Goodbye, Joe!" (Of course, since Joe has already left, he won't see the message, but other users in the channel will.)
Reference:
Brian Seitz, What is IRC bot, Retrieve 11/10/2001
URL:
Tuesday, 8 November 2011
Knowbots
 A kind of bot that collects information by automatically gathering certain specified information from websites. A knowbot is more frequently called an intelligent agent or simply an agent. A knowbot should not be confused with a search engine crawler or spider. A crawler or spider progam visits Web sites and gathers information according to some generalized criteria and this information is then indexed so that it can be used for searching by many individual users. A knowbot works with specific and easily changed criteria that conform to or anticipate the needs of the user or users. Its results are then organized for presentation but not necessarily for searching. An example would be a knowbot (sometimes also called a newsbot) that visited major news-oriented Web sites each morning and provided a digest of stories (or links to them) for a personalized news page.
A kind of bot that collects information by automatically gathering certain specified information from websites. A knowbot is more frequently called an intelligent agent or simply an agent. A knowbot should not be confused with a search engine crawler or spider. A crawler or spider progam visits Web sites and gathers information according to some generalized criteria and this information is then indexed so that it can be used for searching by many individual users. A knowbot works with specific and easily changed criteria that conform to or anticipate the needs of the user or users. Its results are then organized for presentation but not necessarily for searching. An example would be a knowbot (sometimes also called a newsbot) that visited major news-oriented Web sites each morning and provided a digest of stories (or links to them) for a personalized news page.Knowbots Information Service
The Knowbot Information Service (KIS), also known as netaddress, provides a uniform user interface to a variety of remote directory services such as whois, finger, X.500, MCIMail. By submitting a single query to KIS, a user can search a set of remote white pages services and see the results of the search in a uniform format.There are several interfaces to the KIS service including e-mail and telnet. Another KIS interface imitates the Berkeley whois command.
KIS consists of two distinct types of modules which interact with each other (typically across a network) to provide the service. One module is a user agent module that runs on the KIS mail host machine. The second module is a remote server module (possibly on a different machine) that interrogates various database services across the network and provides the results to the user agent module in a uniform fashion. Interactions between the two modules can be via messages between Knowbots or by actual movement of Knowbots.
Reference
Denis Howe, knowbots, Retrieved in 19 June 1999
Friday, 4 November 2011
New ZeuS bot could be antivirus-proof
A modified version of the ZeuS bot may have some appeal to cybercriminals due to its potential to thwart anti-virus software, a computer security firm disclosed.
Trend Micro said the variant, detected as TSPY_ZBOT.IMQU, uses a new encryption-decryption algorithm and makes it harder for anti-virus programs to clean its infection.
“If a machine is infected with ZeuS, calling (API GetFileAttributesExW) via a specific parameter would return with the bot information, which includes bot name, bot version, and a pointer to a function that will uninstall the bot. Antivirus software may utilize this function to identify ZeuS bot information and to clean ZeuS infection automatically. However, the new version of ZeuS also updated this functionality and removed the pointer to the bot uninstall function, thus, eliminating the opportunities for AVs to utilize this function," it said in a blog post.
Also, it said this new version showed current trackers may fail to decrypt its configuration file due to its updated encryption/decryption routine.
The new variant does not use RC4 encryption algorithm but an updated encryption/decryption algorithm instead, Trend Micro added.
Trend Micro said the new malware targets a wide selection of financial firms including those in the United States, Spain, Brazil, Germany, Belgium, France, Italy, and Ireland.
It added the emergence of these latest ZeuS variants implies ZeuS is still a very profitable piece of malware and that cybercriminals are continuously investing on the leaked source code.
Credits to:
http://www.gmanews.tv/story/231604/technology/new-zeus-bot-could-be-antivirus-proof
Trend Micro said the variant, detected as TSPY_ZBOT.IMQU, uses a new encryption-decryption algorithm and makes it harder for anti-virus programs to clean its infection.
“If a machine is infected with ZeuS, calling (API GetFileAttributesExW) via a specific parameter would return with the bot information, which includes bot name, bot version, and a pointer to a function that will uninstall the bot. Antivirus software may utilize this function to identify ZeuS bot information and to clean ZeuS infection automatically. However, the new version of ZeuS also updated this functionality and removed the pointer to the bot uninstall function, thus, eliminating the opportunities for AVs to utilize this function," it said in a blog post.
Also, it said this new version showed current trackers may fail to decrypt its configuration file due to its updated encryption/decryption routine.
The new variant does not use RC4 encryption algorithm but an updated encryption/decryption algorithm instead, Trend Micro added.
We believe this is a private version of a modified ZeuS and is created by a private professional gang comparable to LICAT. Though we have yet to see someone sell this new version of toolkit on underground forums, we expect that we will see more similar variants which will emerge in the not-so-distant future,it said.
Trend Micro said the new malware targets a wide selection of financial firms including those in the United States, Spain, Brazil, Germany, Belgium, France, Italy, and Ireland.
More interestingly, it targets HSBC Hong Kong, which suggests that this new Zeus variant may be used in a global campaign, which may already include Asian countries, it said again.
It added the emergence of these latest ZeuS variants implies ZeuS is still a very profitable piece of malware and that cybercriminals are continuously investing on the leaked source code.
Credits to:
http://www.gmanews.tv/story/231604/technology/new-zeus-bot-could-be-antivirus-proof
Thursday, 3 November 2011
Sixth Poll Result Analysis

This picture below is previous week poll analysis. The tittle of the poll analysis is "Is the Web bot predict by tracing keyword relates to the word you want?". Most of the voters voted "Sometimes only".
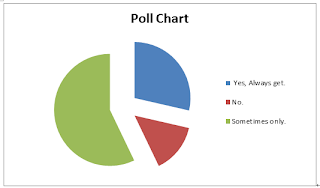
In the conclusion , there are 7 persons voted the poll, 4 persons voted "Sometimes only.". That's mean in the most of the time, web bot keyword prediction is not always help for most of the people., 2 persons voted "Yes, Always get", it's actually web bot keyword prediction is also really helpful for some people.and 1 person voted "No.". If you have any question u can send a mail to us to leave a comment here. Besides, we will always share more information about Web bot to you!
Tuesday, 1 November 2011
Yahoo Bot

The Yahoo! Search engines like Yahoo! crawl through websites to gather information, returning a list of relevant websites to the user who types search terms into them. Bots return up-to-date information on currently active websites but have been known to return defunct websites.
Yahoo! Slurp
Yahoo! Slurp is the recognized name of the bot that the Yahoo! search engine uses. It's a different bot than Googlebot for Google and Bingbot for Bing. Yahoo! Slurp is based on Web crawler architecture developed for Inktomi. The Yahoo! Slurp bot crawls through websites and creates a virtual copy of them to be used later for the search engine.
Bot Tasks
The Yahoo! Slurp bot performs three basic actions for the Yahoo! search engine. First, it retrieves Web server website information. Then the bot analyzes the website content for relevant information. Finally, it files the information to be used in site indexing. The bot itself is little more than an automated script performing these three tasks over and over. However, it can do it at incredibly fast speeds. A Yahoo! search engine results page takes mere seconds to load. It wouldn't be possible without the bot.
Site Indexing
The process of ordering the websites that the Yahoo! Slurp bot has found is called site indexing. Websites are ranked according to their relevancy to search terms and their individual ranks within the Yahoo! search engine. The more popular and integral to the Internet the site is, the more rank it obtains and the higher it is when Yahoo! returns its search results. The Yahoo! Slurp bot helps index the sites for Yahoo!
How the Bot Searches
The Yahoo! Slurp bot uses four parameters when accomplishing its website information retrieval process. It operates using a selection policy that determines which Web pages to download; it uses a re-visit policy that determines when the pages are checked for updated information. The bot also operates by a politeness policy that prevents certain websites from being overloaded with searching. It also operates by a parallelization policy, which coordinates the Yahoo! Slurp bot with other Web crawlers.
Reference
Meg North,What Is a Bot on Yahoo?, Retrieve in 06 september 2011
URL:
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
